Defines a C++ wrapper facade for the Internet domain address family format. More...
#include <INET_Addr.h>
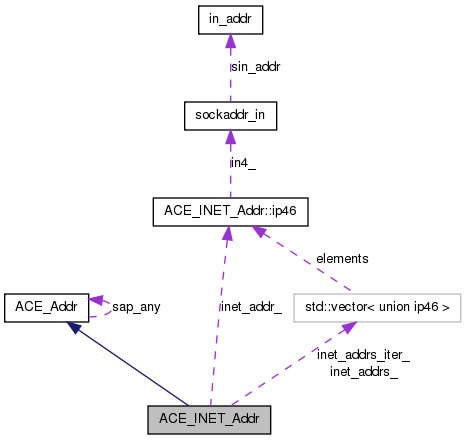
Classes | |
| union | ip46 |
Public Member Functions | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (void) | |
| Default constructor. | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const ACE_INET_Addr &) | |
| Copy constructor. | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const sockaddr_in *addr, int len) | |
| Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a sockaddr_in structure. | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (u_short port_number, const char host_name[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const char address[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (u_short port_number, ACE_UINT32 ip_addr=INADDR_ANY) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const char port_name[], const char host_name[], const char protocol[]="tcp") | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const char port_name[], ACE_UINT32 ip_addr, const char protocol[]="tcp") | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (u_short port_number, const wchar_t host_name[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const wchar_t address[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const wchar_t port_name[], const wchar_t host_name[], const wchar_t protocol[]=ACE_TEXT_WIDE("tcp")) | |
| ACE_INET_Addr (const wchar_t port_name[], ACE_UINT32 ip_addr, const wchar_t protocol[]=ACE_TEXT_WIDE("tcp")) | |
| ~ACE_INET_Addr (void) | |
| Default dtor. | |
| ACE_INET_Addr & | operator= (const ACE_INET_Addr &rhs) |
| int | set (const ACE_INET_Addr &) |
| Initializes from another ACE_INET_Addr. | |
| int | set (u_short port_number, const char host_name[], int encode=1, int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) |
| int | set (u_short port_number, ACE_UINT32 ip_addr=INADDR_ANY, int encode=1, int map=0) |
| int | set (const char port_name[], const char host_name[], const char protocol[]="tcp") |
| int | set (const char port_name[], ACE_UINT32 ip_addr, const char protocol[]="tcp") |
| int | set (const char addr[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) |
| int | set (const sockaddr_in *, int len) |
| Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a sockaddr_in structure. | |
| int | set (u_short port_number, const wchar_t host_name[], int encode=1, int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) |
| int | set (const wchar_t port_name[], const wchar_t host_name[], const wchar_t protocol[]=ACE_TEXT_WIDE("tcp")) |
| int | set (const wchar_t port_name[], ACE_UINT32 ip_addr, const wchar_t protocol[]=ACE_TEXT_WIDE("tcp")) |
| int | set (const wchar_t addr[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) |
| virtual void * | get_addr (void) const |
| Return a pointer to the underlying network address. | |
| int | get_addr_size (void) const |
| virtual void | set_addr (const void *, int len) |
| Set a pointer to the address. | |
| virtual void | set_addr (const void *, int len, int map) |
| Set a pointer to the address. | |
| virtual int | addr_to_string (ACE_TCHAR buffer[], size_t size, int ipaddr_format=1) const |
| virtual int | string_to_addr (const char address[], int address_family=AF_UNSPEC) |
| void | set_port_number (u_short, int encode=1) |
| int | set_address (const char *ip_addr, int len, int encode=1, int map=0) |
| int | set_interface (const char *intf_name) |
| u_short | get_port_number (void) const |
| Return the port number, converting it into host byte-order. | |
| int | get_host_name (char hostname[], size_t hostnamelen) const |
| int | get_host_name (wchar_t hostname[], size_t hostnamelen) const |
| const char * | get_host_name (void) const |
| const char * | get_host_addr (char *addr, int addr_size) const |
| const char * | get_host_addr (void) const |
| ACE_UINT32 | get_ip_address (void) const |
| bool | is_any (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is INADDR_ANY or IN6ADDR_ANY. | |
| bool | is_loopback (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4/IPv6 loopback address. | |
| bool | is_multicast (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4/IPv6 multicast address. | |
| bool | is_linklocal (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is IPv6 linklocal address. | |
| bool | is_ipv4_mapped_ipv6 (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4-mapped IPv6 address. | |
| bool | is_ipv4_compat_ipv6 (void) const |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4-compatible IPv6 address. | |
| bool | operator< (const ACE_INET_Addr &rhs) const |
| bool | operator== (const ACE_INET_Addr &SAP) const |
| bool | operator!= (const ACE_INET_Addr &SAP) const |
| Compare two addresses for inequality. | |
| bool | is_ip_equal (const ACE_INET_Addr &SAP) const |
| virtual u_long | hash (void) const |
| Computes and returns hash value. | |
| bool | next (void) |
| void | reset (void) |
| Reset the set of address so they can be scanned again using next(). | |
| void | dump (void) const |
| Dump the state of an object. | |
Public Attributes | |
| ACE_ALLOC_HOOK_DECLARE | |
| Declare the dynamic allocation hooks. | |
Private Member Functions | |
| int | get_host_name_i (char hostname[], size_t hostnamelen) const |
| Insure that hostname is properly null-terminated. | |
| void * | ip_addr_pointer (void) const |
| int | ip_addr_size (void) const |
| int | determine_type (void) const |
| void | reset_i (void) |
| Initialize underlying inet_addr_ to default values. | |
Private Attributes | |
| union ACE_INET_Addr::ip46 | inet_addr_ |
| std::vector< union ip46 > | inet_addrs_ |
| std::vector< union ip46 >::iterator | inet_addrs_iter_ |
Defines a C++ wrapper facade for the Internet domain address family format.
ACE_INET_Addr can hold all of the IP addresses assigned to a single name. By default it refers only to the first, if there is more than one. The next() method can make the others available in turn.
Definition at line 36 of file INET_Addr.h.
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | void | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 177 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00178 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00179 { 00180 // ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00181 this->reset_i (); 00182 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | sa | ) |
Copy constructor.
Definition at line 321 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const sockaddr_in * | addr, | |
| int | len | |||
| ) |
Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a sockaddr_in structure.
Definition at line 681 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00682 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00683 { 00684 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00685 this->set (addr, len); 00686 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| const char | host_name[], | |||
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) |
Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_number and the remote host_name. The port number is assumed to be in host byte order. To set a port already in network byte order, please
Definition at line 559 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00562 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00563 { 00564 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00565 ACE_OS::memset (&this->inet_addr_, 0, sizeof (this->inet_addr_)); 00566 if (this->set (port_number, 00567 host_name, 00568 1, 00569 address_family) == -1) 00570 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00571 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr: %p\n"), 00572 ACE_TEXT_CHAR_TO_TCHAR ((host_name == 0) ? 00573 "<unknown>" : host_name))); 00574 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const char | address[], | |
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Initializes an ACE_INET_Addr from the address, which can be "ip-number:port-number" (e.g., "tango.cs.wustl.edu:1234" or "128.252.166.57:1234"). If there is no ':' in the address it is assumed to be a port number, with the IP address being INADDR_ANY.
Definition at line 302 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00303 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00304 { 00305 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00306 this->set (address, address_family); 00307 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr = INADDR_ANY | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_number and an Internet ip_addr. This method assumes that port_number and ip_addr are in host byte order. If you have addressing information in network byte order,
Definition at line 690 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00692 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00693 { 00694 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00695 if (this->set (port_number, inet_address) == -1) 00696 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00697 ACE_TEXT ("%p\n"), 00698 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"))); 00699 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const char | port_name[], | |
| const char | host_name[], | |||
| const char | protocol[] = "tcp" | |||
| ) |
Uses getservbyname() to create an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_name, the remote host_name, and the protocol.
Definition at line 704 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00707 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00708 { 00709 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00710 if (this->set (port_name, 00711 host_name, 00712 protocol) == -1) 00713 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00714 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"))); 00715 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const char | port_name[], | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr, | |||
| const char | protocol[] = "tcp" | |||
| ) |
Uses getservbyname() to create an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_name, an Internet ip_addr, and the protocol. This method assumes that ip_addr is in host byte order.
Definition at line 734 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00737 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00738 { 00739 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00740 if (this->set (port_name, 00741 ACE_HTONL (inet_address), 00742 protocol) == -1) 00743 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00744 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"))); 00745 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| const wchar_t | host_name[], | |||
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 577 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00580 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00581 { 00582 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00583 ACE_OS::memset (&this->inet_addr_, 0, sizeof (this->inet_addr_)); 00584 if (this->set (port_number, 00585 host_name, 00586 1, 00587 address_family) == -1) 00588 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00589 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr: %p\n"), 00590 ACE_TEXT_WCHAR_TO_TCHAR ((host_name == 0) ? 00591 ACE_TEXT_WIDE ("<unknown>") : 00592 host_name))); 00593 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const wchar_t | address[], | |
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) | [explicit] |
Definition at line 310 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00311 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00312 { 00313 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00314 this->set (address, address_family); 00315 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const wchar_t | port_name[], | |
| const wchar_t | host_name[], | |||
| const wchar_t | protocol[] = ACE_TEXT_WIDE ("tcp") | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 718 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00721 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00722 { 00723 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00724 if (this->set (port_name, 00725 host_name, 00726 protocol) == -1) 00727 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00728 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"))); 00729 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr | ( | const wchar_t | port_name[], | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr, | |||
| const wchar_t | protocol[] = ACE_TEXT_WIDE ("tcp") | |||
| ) |
Definition at line 748 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00751 : ACE_Addr (determine_type (), sizeof (inet_addr_)) 00752 { 00753 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"); 00754 if (this->set (port_name, 00755 ACE_HTONL (inet_address), 00756 protocol) == -1) 00757 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 00758 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::ACE_INET_Addr"))); 00759 }
| ACE_INET_Addr::~ACE_INET_Addr | ( | void | ) |
| int ACE_INET_Addr::addr_to_string | ( | ACE_TCHAR | buffer[], | |
| size_t | size, | |||
| int | ipaddr_format = 1 | |||
| ) | const [virtual] |
Transform the current ACE_INET_Addr address into string format. If ipaddr_format is true this produces "ip-number:port-number" (e.g., "128.252.166.57:1234"), whereas if ipaddr_format is false this produces "ip-name:port-number" (e.g., "tango.cs.wustl.edu:1234"). Returns -1 if the size of the buffer is too small, else 0.
Definition at line 30 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00033 { 00034 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::addr_to_string"); 00035 00036 // XXX Can we (should we) include the scope id for IPv6 addresses? 00037 char hoststr[MAXHOSTNAMELEN+1]; 00038 00039 bool result = false; 00040 if (ipaddr_format == 0) 00041 result = (this->get_host_name (hoststr, MAXHOSTNAMELEN+1) == 0); 00042 else 00043 result = (this->get_host_addr (hoststr, MAXHOSTNAMELEN+1) != 0); 00044 00045 if (!result) 00046 return -1; 00047 00048 size_t total_len = 00049 ACE_OS::strlen (hoststr) 00050 + 5 // ACE_OS::strlen ("65535"), Assuming the max port number. 00051 + 1 // sizeof (':'), addr/port sep 00052 + 1; // sizeof ('\0'), terminating NUL 00053 #if !defined (ACE_WIN32) && defined (ACE_USES_WCHAR) 00054 ACE_TCHAR const *format = ACE_TEXT("%ls:%d"); 00055 #else 00056 ACE_TCHAR const *format = ACE_TEXT("%s:%d"); 00057 #endif /* !ACE_WIN32 && ACE_USES_WCHAR */ 00058 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00059 if (ACE_OS::strchr (hoststr, ACE_TEXT (':')) != 0) 00060 { 00061 total_len += 2; // ACE_OS::strlen ("[]") IPv6 addr frames 00062 # if !defined (ACE_WIN32) && defined (ACE_USES_WCHAR) 00063 format = ACE_TEXT("[%ls]:%d"); 00064 # else 00065 format = ACE_TEXT("[%s]:%d"); 00066 # endif /* !ACE_WIN32 && ACE_USES_WCHAR */ 00067 } 00068 #endif // ACE_HAS_IPV6 00069 00070 if (size < total_len) 00071 return -1; 00072 else 00073 ACE_OS::snprintf (s, size, format, 00074 ACE_TEXT_CHAR_TO_TCHAR (hoststr), 00075 this->get_port_number ()); 00076 return 0; 00077 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::determine_type | ( | void | ) | const [inline, private] |
Definition at line 35 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00036 { 00037 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00038 # if defined (ACE_USES_IPV4_IPV6_MIGRATION) 00039 return ACE::ipv6_enabled () ? AF_INET6 : AF_INET; 00040 # else 00041 return AF_INET6; 00042 # endif /* ACE_USES_IPV4_IPV6_MIGRATION */ 00043 #else 00044 return AF_INET; 00045 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00046 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::dump | ( | void | ) | const |
Dump the state of an object.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 80 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00081 { 00082 #if defined (ACE_HAS_DUMP) 00083 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::dump"); 00084 00085 ACELIB_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_BEGIN_DUMP, this)); 00086 00087 ACE_TCHAR s[ACE_MAX_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAME_LEN + 16]; 00088 this->addr_to_string(s, ACE_MAX_FULLY_QUALIFIED_NAME_LEN + 16); 00089 ACELIB_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_TEXT ("%s"), s)); 00090 ACELIB_DEBUG ((LM_DEBUG, ACE_END_DUMP)); 00091 #endif /* ACE_HAS_DUMP */ 00092 }
| void * ACE_INET_Addr::get_addr | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Return a pointer to the underlying network address.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 632 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00633 { 00634 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_addr"); 00635 return (void*)&this->inet_addr_; 00636 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::get_addr_size | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Definition at line 99 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00100 { 00101 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_addr_size"); 00102 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00103 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET) 00104 return sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_; 00105 else 00106 return sizeof this->inet_addr_.in6_; 00107 #else 00108 return sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_; 00109 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00110 }
| const char * ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_addr | ( | void | ) | const |
Return the "dotted decimal" Internet address representation of the hostname. This version is non-reentrant since it returns a pointer to a static data area. You should therefore either (1) do a "deep copy" of the address returned by get_host_addr(), e.g., using strdup() or (2) use the "reentrant" version of get_host_addr() described above.
Definition at line 1093 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
01094 { 01095 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_addr"); 01096 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 01097 static char buf[INET6_ADDRSTRLEN]; 01098 return this->get_host_addr (buf, INET6_ADDRSTRLEN); 01099 #else /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 01100 static char buf[INET_ADDRSTRLEN]; 01101 return this->get_host_addr (buf, INET_ADDRSTRLEN); 01102 #endif /* !ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 01103 }
| const char * ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_addr | ( | char * | addr, | |
| int | addr_size | |||
| ) | const |
Return the "dotted decimal" Internet address representation of the hostname storing it in the addr (which is assumed to be addr_size bytes long). This version is reentrant.
Definition at line 1033 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
01034 { 01035 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 01036 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 01037 { 01038 // mcorino@remedy.nl - Aug-26, 2005 01039 // I don't think this should be done because it results in a decimal address 01040 // representation which is not distinguishable from the IPv4 form which makes 01041 // it impossible to resolve back to an IPv6 INET_Addr without prior knowledge 01042 // that this was such an address to begin with. 01043 01044 //if (IN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPED (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr)) 01045 //{ 01046 // ACE_UINT32 addr; 01047 // addr = this->get_ip_address(); 01048 // addr = ACE_HTONL (addr); 01049 // return ACE_OS::inet_ntop (AF_INET, &addr, dst, size); 01050 //} 01051 01052 # if defined (ACE_WIN32) 01053 sockaddr *sa = reinterpret_cast<sockaddr *> 01054 (const_cast<sockaddr_in6 *> (&this->inet_addr_.in6_)); 01055 if (ACE_OS::getnameinfo (sa, this->get_size (), dst, size, 01056 0, 0, // Don't want service name 01057 NI_NUMERICHOST) == 0) 01058 return dst; 01059 ACE_OS::set_errno_to_wsa_last_error (); 01060 return 0; 01061 # else 01062 const char *ch = ACE_OS::inet_ntop (AF_INET6, 01063 &this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr, 01064 dst, 01065 size); 01066 #if defined (ACE_LINUX) 01067 if ((IN6_IS_ADDR_LINKLOCAL (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr) || 01068 IN6_IS_ADDR_MC_LINKLOCAL (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr)) && 01069 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id != 0) 01070 { 01071 char scope_buf[32]; 01072 ACE_OS::snprintf (scope_buf, 32, "%%%u", 01073 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id); 01074 if ((ACE_OS::strlen (ch)+ACE_OS::strlen (scope_buf)) < (size_t)size) 01075 { 01076 ACE_OS::strcat (dst, scope_buf); 01077 } 01078 } 01079 #endif 01080 return ch; 01081 # endif /* ACE_WIN32 */ 01082 } 01083 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 01084 01085 return ACE_OS::inet_ntop (AF_INET, 01086 &this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr, 01087 dst, 01088 size); 01089 }
| const char * ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name | ( | void | ) | const |
Return the character representation of the hostname. This version is non-reentrant since it returns a pointer to a static data area. You should therefore either (1) do a "deep copy" of the address returned by get_host_name(), e.g., using strdup() or (2) use the "reentrant" version of get_host_name() described above.
Definition at line 827 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00828 { 00829 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name"); 00830 00831 static char name[MAXHOSTNAMELEN + 1]; 00832 if (this->get_host_name (name, MAXHOSTNAMELEN + 1) == -1) 00833 ACE_OS::strcpy (name, "<unknown>"); 00834 return name; 00835 }
Definition at line 801 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00803 { 00804 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name"); 00805 00806 char char_hostname [MAXHOSTNAMELEN + 1]; 00807 00808 // We have a build in limitation of MAXHOSTNAMELEN 00809 if (len > MAXHOSTNAMELEN + 1) 00810 len = MAXHOSTNAMELEN + 1; 00811 00812 // Call the char version 00813 int result = this->get_host_name (char_hostname, len); 00814 00815 // And copy it over, if successful 00816 if (result == 0) 00817 ACE_OS::strcpy (hostname, 00818 ACE_Ascii_To_Wide (char_hostname).wchar_rep ()); 00819 00820 return result; 00821 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name | ( | char | hostname[], | |
| size_t | hostnamelen | |||
| ) | const |
Return the character representation of the name of the host, storing it in the hostname (which is assumed to be hostnamelen bytes long). This version is reentrant. If hostnamelen is greater than 0 then hostname will be NUL-terminated even if -1 is returned.
Definition at line 767 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00769 { 00770 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name"); 00771 00772 int result; 00773 if (len > 1) 00774 { 00775 result = this->get_host_name_i (hostname,len); 00776 if (result < 0) 00777 { 00778 if (result == -2) 00779 // We know that hostname is nul-terminated 00780 result = -1; 00781 else 00782 { 00783 //result == -1; 00784 // This could be worse than hostname[len -1] = '\0'? 00785 hostname[0] = '\0'; 00786 } 00787 } 00788 } 00789 else 00790 { 00791 if (len == 1) 00792 hostname[0] = '\0'; 00793 result = -1; 00794 } 00795 00796 return result; 00797 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name_i | ( | char | hostname[], | |
| size_t | hostnamelen | |||
| ) | const [private] |
Insure that hostname is properly null-terminated.
Definition at line 870 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00871 { 00872 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_host_name_i"); 00873 00874 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00875 if ((this->get_type () == PF_INET6 && 00876 0 == ACE_OS::memcmp (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr, 00877 &in6addr_any, 00878 sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr))) 00879 || 00880 (this->get_type () == PF_INET && 00881 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr == INADDR_ANY)) 00882 #else 00883 if (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr == INADDR_ANY) 00884 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00885 return (ACE_OS::hostname (hostname, len) == -1) ? -1 : 0; 00886 00887 const ACE_SOCKET_LEN addr_size = 00888 #ifdef ACE_HAS_IPV6 00889 (this->get_type () == PF_INET6) ? sizeof (sockaddr_in6) : 00890 #endif 00891 sizeof (sockaddr_in); 00892 00893 const int res = ACE_OS::getnameinfo ((const sockaddr *) this->get_addr (), 00894 addr_size, hostname, 00895 static_cast<ACE_SOCKET_LEN> (len), 00896 0, 0, 0); 00897 return (res == 0) ? 0 : -1; 00898 }
| ACE_UINT32 ACE_INET_Addr::get_ip_address | ( | void | ) | const |
Return the 4-byte IP address, converting it into host byte order.
Definition at line 1107 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
01108 { 01109 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_ip_address"); 01110 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 01111 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 01112 { 01113 if (IN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPED (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr) || 01114 IN6_IS_ADDR_V4COMPAT (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr) ) 01115 { 01116 ACE_UINT32 addr; 01117 // Return the last 32 bits of the address 01118 char *thisaddrptr = (char*)this->ip_addr_pointer (); 01119 thisaddrptr += 128/8 - 32/8; 01120 ACE_OS::memcpy (&addr, thisaddrptr, sizeof (addr)); 01121 return ACE_NTOHL (addr); 01122 } 01123 01124 ACELIB_ERROR ((LM_ERROR, 01125 ACE_TEXT ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_ip_address: address is a IPv6 address not IPv4\n"))); 01126 errno = EAFNOSUPPORT; 01127 return 0; 01128 } 01129 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 01130 return ACE_NTOHL (ACE_UINT32 (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr)); 01131 }
| u_short ACE_INET_Addr::get_port_number | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return the port number, converting it into host byte-order.
Definition at line 81 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00082 { 00083 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::get_port_number"); 00084 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00085 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET) 00086 return ACE_NTOHS (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_port); 00087 else 00088 return ACE_NTOHS (this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_port); 00089 #else 00090 # if defined (ACE_VXWORKS) && ACE_VXWORKS >= 0x690 00091 return static_cast<u_short> (ACE_NTOHS (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_port)); 00092 # else 00093 return ACE_NTOHS (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_port); 00094 # endif 00095 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00096 }
| u_long ACE_INET_Addr::hash | ( | void | ) | const [virtual] |
Computes and returns hash value.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 145 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00146 { 00147 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00148 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET6) 00149 { 00150 const unsigned int *addr = (const unsigned int*)this->ip_addr_pointer(); 00151 return addr[0] + addr[1] + addr[2] + addr[3] + this->get_port_number(); 00152 } 00153 else 00154 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00155 return this->get_ip_address () + this->get_port_number (); 00156 }
| void * ACE_INET_Addr::ip_addr_pointer | ( | void | ) | const [inline, private] |
Definition at line 49 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00050 { 00051 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00052 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET) 00053 return (void*)&this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr; 00054 else 00055 return (void*)&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr; 00056 #else 00057 return (void*)&this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr; 00058 #endif 00059 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::ip_addr_size | ( | void | ) | const [inline, private] |
Definition at line 62 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00063 { 00064 // Since this size value is used to pass to other host db-type 00065 // functions (gethostbyaddr, etc.) the length is of int type. 00066 // Thus, cast all these sizes back to int. They're all well 00067 // within the range of an int anyway. 00068 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00069 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET) 00070 return static_cast<int> (sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr); 00071 else 00072 return static_cast<int> (sizeof this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00073 #else 00074 return static_cast<int> (sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr); 00075 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00076 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_any | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is INADDR_ANY or IN6ADDR_ANY.
Definition at line 184 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00185 { 00186 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00187 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00188 return IN6_IS_ADDR_UNSPECIFIED (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00189 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00190 00191 return (this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr == INADDR_ANY); 00192 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_ip_equal | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | SAP | ) | const |
A variation of the equality operator, this method only compares the IP address and ignores the port number.
Definition at line 120 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00121 { 00122 if (this->get_type () != sap.get_type () 00123 || this->get_size () != sap.get_size ()) 00124 return false; 00125 00126 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00127 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET6) 00128 { 00129 const unsigned int *addr = 00130 reinterpret_cast<const unsigned int*>(this->ip_addr_pointer()); 00131 const unsigned int *saddr = 00132 reinterpret_cast<const unsigned int*>(sap.ip_addr_pointer()); 00133 return (addr[0] == saddr[0] && 00134 addr[1] == saddr[1] && 00135 addr[2] == saddr[2] && 00136 addr[3] == saddr[3]); 00137 } 00138 else 00139 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00140 return this->get_ip_address () == sap.get_ip_address(); 00141 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_ipv4_compat_ipv6 | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4-compatible IPv6 address.
Definition at line 243 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00244 { 00245 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00246 return IN6_IS_ADDR_V4COMPAT (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00247 00248 return false; 00249 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_ipv4_mapped_ipv6 | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4-mapped IPv6 address.
Definition at line 233 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00234 { 00235 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00236 return IN6_IS_ADDR_V4MAPPED (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00237 00238 return false; 00239 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_linklocal | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is IPv6 linklocal address.
Definition at line 223 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00224 { 00225 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00226 return IN6_IS_ADDR_LINKLOCAL (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00227 00228 return false; 00229 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_loopback | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4/IPv6 loopback address.
Definition at line 196 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00197 { 00198 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00199 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00200 return IN6_IS_ADDR_LOOPBACK (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr); 00201 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00202 00203 // RFC 3330 defines loopback as any address with 127.x.x.x 00204 return ((this->get_ip_address () & 0XFF000000) == (INADDR_LOOPBACK & 0XFF000000)); 00205 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::is_multicast | ( | void | ) | const [inline] |
Return true if the IP address is IPv4/IPv6 multicast address.
Definition at line 209 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00210 { 00211 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00212 if (this->get_type() == AF_INET6) 00213 return this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr.s6_addr[0] == 0xFF; 00214 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00215 return 00216 (*static_cast<const unsigned char*> ( 00217 static_cast<const void*> (&this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr.s_addr)) & 0xf0) == 0xe0; 00218 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::next | ( | void | ) |
If there is another address to examine, move to it and return true; else return false.
Definition at line 159 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00160 { 00161 if (this->inet_addrs_.empty () || 00162 this->inet_addrs_iter_ == this->inet_addrs_.end ()) 00163 return false; 00164 00165 union ip46 next_a = *this->inet_addrs_iter_++; 00166 this->set_addr (&next_a, sizeof (next_a)); 00167 return true; 00168 }
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::operator!= | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | SAP | ) | const |
Compare two addresses for inequality.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 97 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::operator< | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | rhs | ) | const [inline] |
Returns true if this is less than rhs. In this context, "less than" is defined in terms of IP address and TCP port number. This operator makes it possible to use ACE_INET_Addrs in STL maps.
Definition at line 113 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00114 { 00115 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00116 if (this->get_type() != rhs.get_type()) 00117 { 00118 return this->get_type() < rhs.get_type(); 00119 } 00120 00121 if (this->get_type() == PF_INET6) 00122 { 00123 int memval = ACE_OS::memcmp (this->ip_addr_pointer(), 00124 rhs.ip_addr_pointer(), 00125 this->ip_addr_size()); 00126 00127 return memval < 0 00128 || (memval == 0 00129 && (this->get_port_number() < rhs.get_port_number() 00130 || (this->get_port_number() == rhs.get_port_number() 00131 && this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id < 00132 rhs.inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id))); 00133 } 00134 #endif 00135 00136 return this->get_ip_address () < rhs.get_ip_address () 00137 || (this->get_ip_address () == rhs.get_ip_address () 00138 && this->get_port_number () < rhs.get_port_number ()); 00139 }
| ACE_INET_Addr & ACE_INET_Addr::operator= | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | rhs | ) |
Assignment. In a more well-ordered world, member-wise assignment would work fine. However, because of the class design feature that all of the acceptor/connector-type classes that can be used in the Acceptor-Connector framework take ACE_Addr objects instead of the addressing class matching the family in use. The mechanism used to enable this substitution to the more-appropriate class is ACE_sap_any_cast, which casts the ACE_Addr to the more-specific class. In this case, casting an ACE_Addr to ACE_INET_Addr then copying it. Since adding multiple address support to ACE_INET_Addr, that cast-copy operation ends up, in the member-wise case, copying a bogus vector and doing lots of random damage. Thus, this operator is used to make life ordered in this common scenario.
Definition at line 185 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
| bool ACE_INET_Addr::operator== | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | SAP | ) | const |
Compare two addresses for equality. The addresses are considered equal if they contain the same IP address and port number.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 106 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00107 { 00108 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::operator =="); 00109 00110 if (this->get_type () != sap.get_type () 00111 || this->get_size () != sap.get_size ()) 00112 return false; 00113 00114 return (ACE_OS::memcmp (&this->inet_addr_, 00115 &sap.inet_addr_, 00116 this->get_size ()) == 0); 00117 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::reset | ( | void | ) |
Reset the set of address so they can be scanned again using next().
Definition at line 171 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00172 { 00173 this->inet_addrs_iter_ = this->inet_addrs_.begin (); 00174 this->next (); 00175 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::reset_i | ( | void | ) | [inline, private] |
Initialize underlying inet_addr_ to default values.
Definition at line 10 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00011 { 00012 ACE_OS::memset (&this->inet_addr_, 0, sizeof (this->inet_addr_)); 00013 if (this->get_type() == AF_INET) 00014 { 00015 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN_SIN_LEN 00016 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00017 #endif 00018 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_family = AF_INET; 00019 } 00020 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00021 else if (this->get_type() == AF_INET6) 00022 { 00023 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN6_SIN6_LEN 00024 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_); 00025 #endif 00026 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_family = AF_INET6; 00027 } 00028 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00029 this->inet_addrs_.clear (); 00030 this->inet_addrs_iter_ = this->inet_addrs_.end (); 00031 00032 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const wchar_t | addr[], | |
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 175 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00176 { 00177 return this->set (ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (addr).char_rep (), address_family); 00178 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const wchar_t | port_name[], | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr, | |||
| const wchar_t | protocol[] = ACE_TEXT_WIDE ("tcp") | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 165 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00168 { 00169 return this->set (ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (port_name).char_rep (), 00170 ip_addr, 00171 ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (protocol).char_rep ()); 00172 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const wchar_t | port_name[], | |
| const wchar_t | host_name[], | |||
| const wchar_t | protocol[] = ACE_TEXT_WIDE ("tcp") | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 155 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00158 { 00159 return this->set (ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (port_name).char_rep (), 00160 ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (host_name).char_rep (), 00161 ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (protocol).char_rep ()); 00162 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| const wchar_t | host_name[], | |||
| int | encode = 1, |
|||
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Definition at line 143 of file INET_Addr.inl.
00147 { 00148 return this->set (port_number, 00149 ACE_Wide_To_Ascii (host_name).char_rep (), 00150 encode, 00151 address_family); 00152 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const sockaddr_in * | addr, | |
| int | len | |||
| ) |
Creates an ACE_INET_Addr from a sockaddr_in structure.
Definition at line 599 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00600 { 00601 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00602 00603 this->reset_i (); 00604 if (addr->sin_family == AF_INET) 00605 { 00606 int maxlen = static_cast<int> (sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_)); 00607 if (len > maxlen) 00608 len = maxlen; 00609 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in4_, addr, len); 00610 this->base_set (AF_INET, len); 00611 return 0; 00612 } 00613 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00614 else if (addr->sin_family == AF_INET6) 00615 { 00616 int maxlen = static_cast<int> (sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_)); 00617 if (len > maxlen) 00618 len = maxlen; 00619 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in6_, addr, len); 00620 this->base_set (AF_INET6, len); 00621 return 0; 00622 } 00623 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00624 00625 errno = EAFNOSUPPORT; 00626 return -1; 00627 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const char | addr[], | |
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) |
Initializes an ACE_INET_Addr from the addr, which can be "ip-number:port-number" (e.g., "tango.cs.wustl.edu:1234" or "128.252.166.57:1234"). If there is no ':' in the address it is assumed to be a port number, with the IP address being INADDR_ANY.
Definition at line 295 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00296 { 00297 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00298 this->reset_i (); 00299 return this->string_to_addr (address, address_family); 00300 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const char | port_name[], | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr, | |||
| const char | protocol[] = "tcp" | |||
| ) |
Uses getservbyname() to initialize an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_name, an ip_addr, and the protocol. This assumes that ip_addr is already in network byte order.
Definition at line 539 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00542 { 00543 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00544 00545 this->reset_i (); 00546 int const port_number = get_port_number_from_name (port_name, protocol); 00547 if (port_number == -1) 00548 { 00549 ACE_NOTSUP_RETURN (-1); 00550 } 00551 00552 return this->set (static_cast<u_short> (port_number), 00553 inet_address, 0); 00554 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const char | port_name[], | |
| const char | host_name[], | |||
| const char | protocol[] = "tcp" | |||
| ) |
Uses getservbyname() to initialize an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_name, the remote host_name, and the protocol.
Definition at line 509 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00512 { 00513 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00514 00515 this->reset_i (); 00516 int const port_number = get_port_number_from_name (port_name, protocol); 00517 if (port_number == -1) 00518 { 00519 ACE_NOTSUP_RETURN (-1); 00520 } 00521 00522 int address_family = PF_UNSPEC; 00523 if (ACE_OS::strcmp(protocol, "tcp") == 0) 00524 address_family = AF_INET; 00525 00526 # if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00527 if (ACE_OS::strcmp (protocol, "tcp6") == 0) 00528 address_family = AF_INET6; 00529 # endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00530 00531 return this->set (static_cast<u_short> (port_number), 00532 host_name, 0, address_family); 00533 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| ACE_UINT32 | ip_addr = INADDR_ANY, |
|||
| int | encode = 1, |
|||
| int | map = 0 | |||
| ) |
Initializes an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_number and an Internet ip_addr. If encode is non-zero then the port number and IP address are converted into network byte order, otherwise they are assumed to be in network byte order already and are passed straight through.
If map is non-zero and IPv6 support has been compiled in, then this address will be set to the IPv4-mapped IPv6 address of it.
Definition at line 332 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00336 { 00337 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00338 this->reset_i (); 00339 this->set_address (reinterpret_cast<const char *> (&inet_address), 00340 sizeof inet_address, 00341 encode, map); 00342 this->set_port_number (port_number, encode); 00343 00344 return 0; 00345 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| const char | host_name[], | |||
| int | encode = 1, |
|||
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) |
Initializes an ACE_INET_Addr from a port_number and the remote host_name. If encode is non-zero then port_number is converted into network byte order, otherwise it is assumed to be in network byte order already and are passed straight through. address_family can be used to select IPv4/IPv6 if the OS has IPv6 capability (ACE_HAS_IPV6 is defined). To specify IPv6, use the value AF_INET6. To specify IPv4, use AF_INET.
Definition at line 352 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00356 { 00357 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00358 00359 // Yow, someone gave us a NULL host_name! 00360 if (host_name == 0) 00361 { 00362 errno = EINVAL; 00363 return -1; 00364 } 00365 00366 this->reset_i (); 00367 00368 #if defined ACE_HAS_IPV6 && defined ACE_USES_IPV4_IPV6_MIGRATION 00369 if (address_family == AF_UNSPEC && !ACE::ipv6_enabled ()) 00370 address_family = AF_INET; 00371 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 && ACE_USES_IPV4_IPV6_MIGRATION */ 00372 00373 #ifdef ACE_HAS_IPV6 00374 if (address_family == AF_UNSPEC && ACE::ipv6_enabled ()) 00375 address_family = AF_INET6; 00376 00377 if (address_family != AF_INET 00378 && ACE_OS::inet_pton (AF_INET6, host_name, 00379 &this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr) == 1) 00380 { 00381 this->base_set (AF_INET6, sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00382 # ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN6_SIN6_LEN 00383 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_len = sizeof this->inet_addr_.in6_; 00384 # endif 00385 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_family = AF_INET6; 00386 this->set_size (sizeof this->inet_addr_.in6_); 00387 this->set_type (AF_INET6); 00388 this->set_port_number (port_number, encode); 00389 return 0; 00390 } 00391 #else 00392 address_family = AF_INET; 00393 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00394 00395 if (ACE_OS::inet_pton (AF_INET, host_name, 00396 &this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr) == 1) 00397 { 00398 this->base_set (AF_INET, sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00399 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN_SIN_LEN 00400 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_len = sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_; 00401 #endif 00402 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_family = AF_INET; 00403 this->set_size (sizeof this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00404 this->set_type (AF_INET); 00405 this->set_port_number (port_number, encode); 00406 return 0; 00407 } 00408 00409 addrinfo hints; 00410 ACE_OS::memset (&hints, 0, sizeof hints); 00411 hints.ai_family = address_family; 00412 // The ai_flags used to contain AI_ADDRCONFIG as well but that prevented 00413 // lookups from completing if there is no, or only a loopback, IPv6 00414 // interface configured. See Bugzilla 4211 for more info. 00415 00416 hints.ai_flags = AI_V4MAPPED; 00417 #if defined(ACE_HAS_IPV6) && defined(AI_ALL) 00418 // Without AI_ALL, Windows machines exhibit inconsistent behaviors on 00419 // difference machines we have tested. 00420 hints.ai_flags |= AI_ALL; 00421 #endif 00422 00423 // Note - specify the socktype here to avoid getting multiple entries 00424 // returned with the same address for different socket types or 00425 // protocols. If this causes a problem for some reason (an address that's 00426 // available for TCP but not UDP, or vice-versa) this will need to change 00427 // back to unrestricted hints and weed out the duplicate addresses by 00428 // searching this->inet_addrs_ which would slow things down. 00429 hints.ai_socktype = SOCK_STREAM; 00430 00431 addrinfo *res = 0; 00432 const int error = ACE_OS::getaddrinfo (host_name, 0, &hints, &res); 00433 00434 if (error) 00435 { 00436 errno = error; 00437 return -1; 00438 } 00439 00440 this->set_type (res->ai_family); 00441 00442 for (addrinfo *curr = res; curr; curr = curr->ai_next) 00443 { 00444 ip46 addr; 00445 ACE_OS::memcpy (&addr, curr->ai_addr, curr->ai_addrlen); 00446 #ifdef ACE_HAS_IPV6 00447 if (curr->ai_family == AF_INET6) 00448 addr.in6_.sin6_port = encode ? ACE_NTOHS (port_number) : port_number; 00449 else 00450 #endif 00451 addr.in4_.sin_port = encode ? ACE_NTOHS (port_number) : port_number; 00452 this->inet_addrs_.push_back (addr); 00453 } 00454 00455 ACE_OS::freeaddrinfo (res); 00456 this->reset (); 00457 return 0; 00458 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set | ( | const ACE_INET_Addr & | sa | ) |
Initializes from another ACE_INET_Addr.
Definition at line 193 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00194 { 00195 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set"); 00196 00197 if (sa.get_type () == AF_ANY) 00198 // Ugh, this is really a base class, so don't copy it. 00199 ACE_OS::memset (&this->inet_addr_, 0, sizeof (this->inet_addr_)); 00200 else 00201 { 00202 // It's ok to make the copy. 00203 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_, 00204 &sa.inet_addr_, 00205 sa.get_size ()); 00206 00207 this->set_type (sa.get_type()); 00208 this->set_size (sa.get_size()); 00209 this->inet_addrs_ = sa.inet_addrs_; 00210 this->reset (); 00211 } 00212 00213 return 0; 00214 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::set_addr | ( | const void * | addr, | |
| int | len, | |||
| int | map | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Set a pointer to the address.
Definition at line 646 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00647 { 00648 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set_addr"); 00649 const struct sockaddr_in *getfamily = 00650 static_cast<const struct sockaddr_in *> (addr); 00651 00652 if (getfamily->sin_family == AF_INET) 00653 { 00654 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00655 if (map) 00656 this->set_type (AF_INET6); 00657 else 00658 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00659 this->set_type (AF_INET); 00660 this->set_port_number (getfamily->sin_port, 0); 00661 this->set_address (reinterpret_cast<const char*> (&getfamily->sin_addr), 00662 sizeof (getfamily->sin_addr), 00663 0, map); 00664 } 00665 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00666 else if (getfamily->sin_family == AF_INET6) 00667 { 00668 const struct sockaddr_in6 *in6 = 00669 static_cast<const struct sockaddr_in6*> (addr); 00670 this->set_port_number (in6->sin6_port, 0); 00671 this->set_address (reinterpret_cast<const char*> (&in6->sin6_addr), 00672 sizeof (in6->sin6_addr), 00673 0); 00674 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id = in6->sin6_scope_id; 00675 } 00676 #endif // ACE_HAS_IPV6 00677 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::set_addr | ( | const void * | addr, | |
| int | len | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Set a pointer to the address.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Definition at line 639 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00640 { 00641 this->set_addr (addr, len, 0); 00642 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set_address | ( | const char * | ip_addr, | |
| int | len, | |||
| int | encode = 1, |
|||
| int | map = 0 | |||
| ) |
Sets the address without affecting the port number. If encode is enabled then ip_addr is converted into network byte order, otherwise it is assumed to be in network byte order already and are passed straight through. The size of the address is specified in the len parameter. If map is non-zero, IPv6 support has been compiled in, and ip_addr is an IPv4 address, then this address is set to the IPv4-mapped IPv6 address of it.
Definition at line 900 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00904 { 00905 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set_address"); 00906 // This is really intended for IPv4. If the object is IPv4, or the type 00907 // hasn't been set but it's a 4-byte address, go ahead. If this is an 00908 // IPv6 object and <encode> is requested, refuse. 00909 if (encode && len != 4) 00910 { 00911 errno = EAFNOSUPPORT; 00912 return -1; 00913 } 00914 00915 if (len == 4) 00916 { 00917 ACE_UINT32 ip4 = *reinterpret_cast<const ACE_UINT32 *> (ip_addr); 00918 if (encode) 00919 ip4 = ACE_HTONL (ip4); 00920 00921 00922 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET && map == 0) { 00923 this->base_set (AF_INET, sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_)); 00924 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN_SIN_LEN 00925 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00926 #endif 00927 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_family = AF_INET; 00928 this->set_size (sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_)); 00929 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr, 00930 &ip4, 00931 len); 00932 } 00933 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00934 else if (map == 0) 00935 { 00936 // this->set_type (AF_INET); 00937 this->base_set (AF_INET, sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_)); 00938 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN_SIN_LEN 00939 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_); 00940 #endif 00941 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_family = AF_INET; 00942 this->set_size (sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in4_)); 00943 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_addr, 00944 &ip4, len); 00945 } 00946 // If given an IPv4 address to copy to an IPv6 object, map it to 00947 // an IPv4-mapped IPv6 address. 00948 else 00949 { 00950 this->base_set (AF_INET6, sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_)); 00951 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN6_SIN6_LEN 00952 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_); 00953 #endif 00954 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_family = AF_INET6; 00955 this->set_size (sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_)); 00956 if (ip4 == ACE_HTONL (INADDR_ANY)) 00957 { 00958 in6_addr const ip6 = in6addr_any; 00959 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr, 00960 &ip6, 00961 sizeof (ip6)); 00962 return 0; 00963 } 00964 else 00965 { 00966 // Build up a 128 bit address. An IPv4-mapped IPv6 address 00967 // is defined as 0:0:0:0:0:ffff:IPv4_address. This is defined 00968 // in RFC 1884 */ 00969 ACE_OS::memset (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr, 0, 16); 00970 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr.s6_addr[10] = 00971 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr.s6_addr[11] = 0xff; 00972 ACE_OS::memcpy 00973 (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr.s6_addr[12], &ip4, 4); 00974 } 00975 } 00976 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00977 00978 return 0; 00979 } /* end if (len == 4) */ 00980 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00981 else if (len == 16) 00982 { 00983 if (this->get_type () != PF_INET6) 00984 { 00985 errno = EAFNOSUPPORT; 00986 return -1; 00987 } 00988 // We protect ourselves up above so IPv6 must be possible here. 00989 this->base_set (AF_INET6, sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_)); 00990 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_family = AF_INET6; 00991 #ifdef ACE_HAS_SOCKADDR_IN6_SIN6_LEN 00992 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_len = sizeof (this->inet_addr_.in6_); 00993 #endif 00994 ACE_OS::memcpy (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr, ip_addr, len); 00995 return 0; 00996 } /* end len == 16 */ 00997 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00998 00999 // Here with an unrecognized length. 01000 errno = EAFNOSUPPORT; 01001 return -1; 01002 01003 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::set_interface | ( | const char * | intf_name | ) |
Sets the interface that should be used for this address. This only has an effect when the address is link local, otherwise it does nothing.
Definition at line 1007 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
01008 { 01009 if (this->get_type () == PF_INET6 && 01010 (IN6_IS_ADDR_LINKLOCAL (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr) || 01011 IN6_IS_ADDR_MC_LINKLOCAL (&this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_addr))) 01012 { 01013 #if defined (ACE_LINUX) 01014 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id = 01015 ACE_OS::if_nametoindex (intf_name); 01016 #else 01017 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id = 01018 intf_name ? ACE_OS::atoi (intf_name) : 0; 01019 #endif 01020 // check to see if the interface lookup succeeded 01021 if (this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_scope_id != 0) 01022 return 0; 01023 else 01024 return -1; 01025 } 01026 else 01027 return 0; 01028 01029 }
| void ACE_INET_Addr::set_port_number | ( | u_short | port_number, | |
| int | encode = 1 | |||
| ) |
Sets the port number without affecting the host name. If encode is enabled then port_number is converted into network byte order, otherwise it is assumed to be in network byte order already and are passed straight through.
Reimplemented in ACE_Multihomed_INET_Addr.
Definition at line 838 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00840 { 00841 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::set_port_number"); 00842 00843 if (encode) 00844 port_number = ACE_HTONS (port_number); 00845 00846 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00847 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00848 this->inet_addr_.in6_.sin6_port = port_number; 00849 else 00850 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00851 this->inet_addr_.in4_.sin_port = port_number; 00852 00853 if (this->inet_addrs_.empty ()) 00854 return; 00855 for (std::vector<union ip46>::iterator i = this->inet_addrs_.begin (); 00856 i != this->inet_addrs_.end (); 00857 i++) 00858 { 00859 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00860 if (this->get_type () == AF_INET6) 00861 i->in6_.sin6_port = port_number; 00862 else 00863 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00864 i->in4_.sin_port = port_number; 00865 } 00866 }
| int ACE_INET_Addr::string_to_addr | ( | const char | address[], | |
| int | address_family = AF_UNSPEC | |||
| ) | [virtual] |
Initializes an ACE_INET_Addr from the address, which can be "ip-addr:port-number" (e.g., "tango.cs.wustl.edu:1234"), "ip-addr:port-name" (e.g., "tango.cs.wustl.edu:telnet"), "ip-number:port-number" (e.g., "128.252.166.57:1234"), or "ip-number:port-name" (e.g., "128.252.166.57:telnet"). If there is no ':' in the address it is assumed to be a port number, with the IP address being INADDR_ANY.
Definition at line 219 of file INET_Addr.cpp.
00220 { 00221 ACE_TRACE ("ACE_INET_Addr::string_to_addr"); 00222 int result; 00223 char *ip_buf = 0; 00224 char *ip_addr = 0; 00225 00226 // Need to make a duplicate since we'll be overwriting the string. 00227 ACE_ALLOCATOR_RETURN (ip_buf, 00228 ACE_OS::strdup (s), 00229 -1); 00230 ip_addr = ip_buf; 00231 // We use strrchr because of IPv6 addresses. 00232 char *port_p = ACE_OS::strrchr (ip_addr, ':'); 00233 #if defined (ACE_HAS_IPV6) 00234 // Check for extended IPv6 format : '[' <ipv6 address> ']' ':' <port> 00235 if (ip_addr[0] == '[') 00236 { 00237 // find closing bracket 00238 char *cp_pos = ACE_OS::strchr (ip_addr, ']'); 00239 // check for port separator after closing bracket 00240 // if not found leave it, error will come later 00241 if (cp_pos) 00242 { 00243 *cp_pos = '\0'; // blank out ']' 00244 ++ip_addr; // skip over '[' 00245 if (cp_pos[1] == ':') 00246 port_p = cp_pos + 1; 00247 else 00248 port_p = cp_pos; // leads to error on missing port 00249 } 00250 } 00251 #endif /* ACE_HAS_IPV6 */ 00252 00253 if (port_p == 0) // Assume it's a port number. 00254 { 00255 char *endp = 0; 00256 long const port = ACE_OS::strtol (ip_addr, &endp, 10); 00257 00258 if (*endp == '\0') // strtol scanned the entire string - all digits 00259 { 00260 if (port < 0 || port > ACE_MAX_DEFAULT_PORT) 00261 result = -1; 00262 else 00263 result = this->set (u_short (port), ACE_UINT32 (INADDR_ANY)); 00264 } 00265 else // port name 00266 result = this->set (ip_addr, ACE_UINT32 (INADDR_ANY)); 00267 } 00268 else 00269 { 00270 *port_p = '\0'; ++port_p; // skip over ':' 00271 00272 char *endp = 0; 00273 long port = ACE_OS::strtol (port_p, &endp, 10); 00274 00275 if (*endp == '\0') // strtol scanned the entire string - all digits 00276 { 00277 if (port < 0 || port > ACE_MAX_DEFAULT_PORT) 00278 result = -1; 00279 else 00280 result = this->set (u_short (port), ip_addr, 1, address_family); 00281 } 00282 else 00283 result = this->set (port_p, ip_addr); 00284 } 00285 00286 #if defined (ACE_HAS_ALLOC_HOOKS) 00287 ACE_Allocator::instance()->free (ACE_MALLOC_T (ip_buf)); 00288 #else 00289 ACE_OS::free (ACE_MALLOC_T (ip_buf)); 00290 #endif /* ACE_HAS_ALLOC_HOOKS */ 00291 return result; 00292 }
Declare the dynamic allocation hooks.
Reimplemented from ACE_Addr.
Reimplemented in ACE_Multihomed_INET_Addr.
Definition at line 380 of file INET_Addr.h.
union ACE_INET_Addr::ip46 ACE_INET_Addr::inet_addr_ [private] |
Underlying representation. This union uses the knowledge that the two structures share the first member, sa_family (as all sockaddr structures do).
std::vector<union ip46> ACE_INET_Addr::inet_addrs_ [private] |
Definition at line 407 of file INET_Addr.h.
std::vector<union ip46>::iterator ACE_INET_Addr::inet_addrs_iter_ [private] |
Definition at line 408 of file INET_Addr.h.
 1.6.1
1.6.1